The inner ear, containing: Cochlea, vestibular, pulvinar, auditory canals, and ear drum. This has the sensory organs for hearing.
Vestibular. This includes the nerves responsible for balance and hearing. The cochlea contains the auditory nerve. This contains sensors for balance, smell.
Semicircular canal. This is a passageway that connects the eardrum to the inner ear, as well as other parts of the head. In order for sound to reach the brain it must pass through this canal.
Ear drum. It is the most important part of the inner ear, and is the largest structure inside the ear. It is made up of cartilage and bone. It is composed of one or more hair follicles, bones, and skin cells.
Ear wax. It is a substance produced by the body. It serves as an insulator. When it comes in contact with air, the air molecules are attracted to the material. These particles are then filtered by the hair cells and hairs, which trap the air.
Outer ear. This is the exterior surface of the inner ear.
Brain. This is the organ that receives, interprets, and stores information from all the sensory organs in the body. It is responsible for movement, hearing, vision, and speech. It also controls the muscle responses that cause the organs to work properly.
The inner ear is very delicate. The inner ear is not designed to be damaged. It is made up of three layers: The Middle Eustachian Tube, the vestibular membrane, and the Cochlea (inner and outer ear)
The middle eustachian tube is responsible for transmitting information from the brain to the inner ear.
As we listen to an external sound to the auditory nerve sends information from the brain to the middle eustachian tube
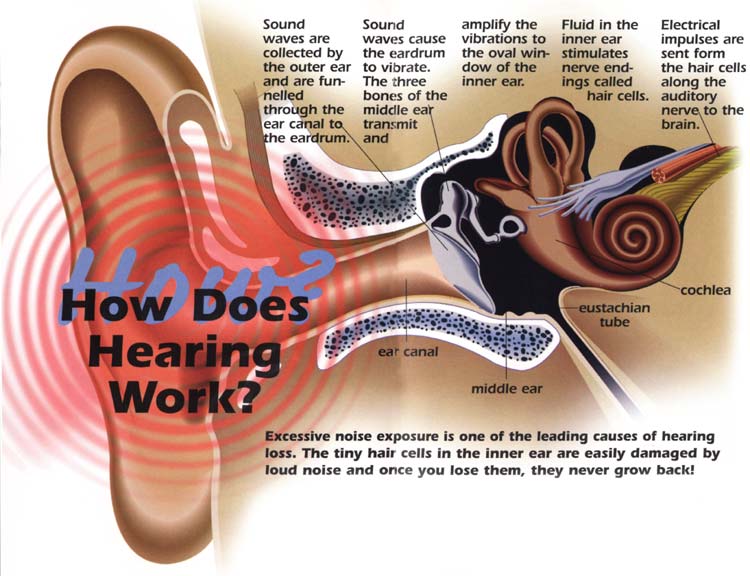
The vestibular membrane, located between the vestibule and cochlea, is responsible for providing information to the brain about the position of the ear. when a person moves his or her head. When an individual listens to external sounds the vestibule and cochlea send information to the brain, which then sends information back to the auditory nerve.
The Cochlea is responsible for producing sounds for the inner ear by releasing and amplifying the sounds that come out of the auditory nerves. A person's hearing is based on vibrations of these noises coming from the outer ear and from the inner ear, which vibrate.
The auditory nerve is responsible for delivering sound signals from the brain to the hearing mechanism. When there is an imbalance in the auditory pathway, hearing loss occurs.
The eardrum provides the body with a mechanism for producing sound. The inner ear is divided into two parts: the cochlea and the vestibular part. The snail is responsible for producing sound waves, and the vestibule is responsible for storing sound.
The ear is made up of three different layers. The ear membrane is made up of cartilage and bone, while the outer ear is made up of cartilage and skin cells. Inner ear structures help maintain normal hearing.
If the inner ear is healthy and properly covered, hearing can be achieved. As mentioned above, good hearing is directly related to good hearing. Proper treatment is a surefire way to prevent deafness or tinnitus.
To better understand the function of the inner ear, you need to know the vestibular system. The vestibular apparatus is responsible for hearing. The ear has two parts: the outer and the inner. The vestibular organ is a small organ located just above the cochlea, near the ear canal. This organ is made up of fluid-filled sacs and hair-like cilia that cover the outer ear.
The vestibular organ is responsible for the production of sound signals from the inner ear. It acts as a sensor to provide directional entry into the auditory system.
The vestibular system consists of two parts: the cochlea, the vestibular organ, and the auditory nerve. Both are responsible for providing a person with a mechanism for the inner ear to receive and process sound.