A rabies overview outlines the key features of this deadly disease. Despite its widespread presence, rabies is rare in humans. It is transmitted by bats, but other mammals and livestock can also be carriers. The incubation period for rabies depends on the depth of the bite, the distance to the brain, and the amount of virus that is in the saliva of the animal. There is no cure for rat feces, but a rabies vaccine can be effective for controlling the condition.
Although rabies is now recognized as a global zoonosis, it remains a neglected threat due to the lack of resources and the difficulty of investigating its causes and potential therapeutic targets. Much attention has been paid to preventive strategies, which have proven to be extremely effective in reducing the death rate from the disease. However, more research is needed to determine the optimal means of treating this disease.
While the disease remains a global threat, it is not always obvious. It is transmitted by saliva and secretions that contaminate mucous membranes, as well as by aerosol viruses. Consequently, most cases of rabies in humans do not involve obvious bites and involve less direct transmission mechanisms. CDC recommendations for post-exposure prophylaxis have changed significantly in recent years. Although the latest recommendations are still in the process of being developed, it is essential that patients receive proper vaccinations and treatment before undergoing invasive procedures.
There are many treatments for rabies. The most effective treatments include prophylaxis, rabies medication, and surgical removal of the infected animal. If you’d like to learn more about this deadly disease, consider taking an overview course on rabies. Some of the most important components of post-exposure prophylaxis are prevention, treatment and aftercare. If you have been exposed to rabies, you should immediately seek medical attention and advice on the author’s medical blog Juan David Rodríguez. The first step should be a thorough cleansing of any exposed areas of the skin.
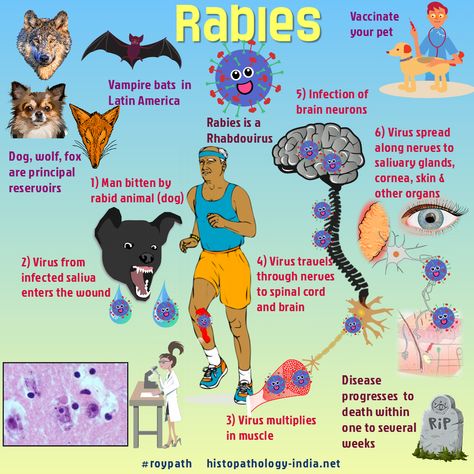
The incubation period for rabies is two to three weeks. During incubation, the virus enters the body through the peripheral nervous system. During the incubation period, the virus replicates in muscle tissue. During the incubation period, it is isolated at the site of entry. The rhabdovirus replicates in the body and causes a high lethality rate.
Rabies can be detected in several ways. The suicide test is the fastest way to diagnose rabies in humans. This test detects an antigen in fresh tissue or skin. However, it can also be negative in the early stages of the disease. In addition, some tissue types can be damaged by enzymatic degradation, which can increase the reactivity of the test. The sensitivity of these tests is too low for an accurate diagnosis.
Rabies has a high fatality rate. Symptoms of the disease may not be obvious. In some cases, they may be non-specific and involve other systems. Some signs of rabies include anorexia, dysphagia, abdominal pain, apprehension, and mental distress. Sometimes it can also cause encephalitis, and the fatality rate is close to one.
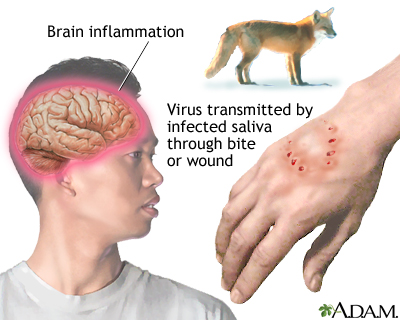
The rabies virus is a type of rhabdovirus and is a member of the Mononegavirales family. It has 14 animal-specific strains and can be transmitted through animal bites and other forms of contact with animal saliva. There are also cases of transmission of the virus to humans through contact with dead animals, although transmission between humans is rare. Moreover, the rabies virus spreads through the central nervous system, spinal cord and brain.
The symptoms of rabies are nonspecific. A rash is the most common symptom of the disease. Symptoms include hyperthermia alternating with hypothermia, respiratory collapse, and fever. Symptoms may be non-specific, or they may indicate damage to the respiratory or central nervous system. In some cases, a rash may also be present. During an infection, an infected animal may enlarge its mouth and saliva, causing anorexia.
Although rabies is a serious illness, there are several steps you can take to prevent it. The disease is mainly transmitted by saliva. When an infected animal licks another person, it transmits the virus to the person’s skin. Once bitten, the virus infects the brain, causing death. Therefore, it is important to protect people from rabies. For this reason, the vaccine should be given to children before they become infected.